Want to export data from Redshift query result to SQL using current date as file name?
Using DB To File, a SQL exporter for Redshift on Windows, MacOS, and Linux, you can export Redshift query result to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time easily.
- Can run in GUI mode, Step by Step, just a few mouse clicks.
- Can run in Command line, for Scheduled Tasks and Streams.
Export Redshift query result to SQL file using dynamic filename with date and time
Login to Redshift -> Enter Redshift SQL statement -> Set SQL filename template including date -> Export Redshift query to SQL using current date as file name
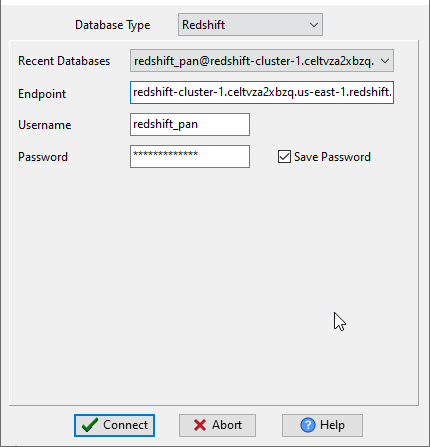
Choose Redshift and logon.
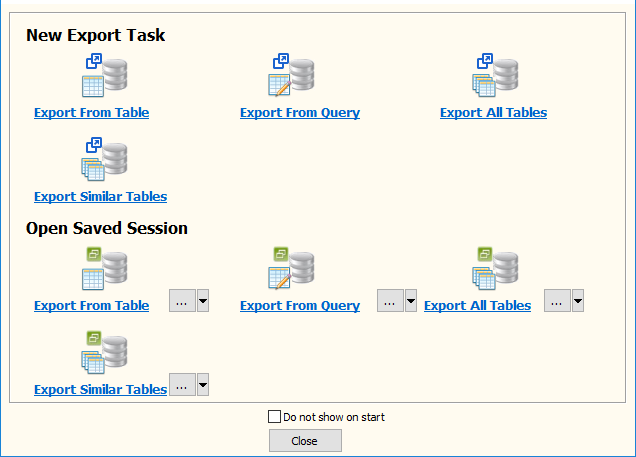
“Export From Query” for “SQL to Redshift“.
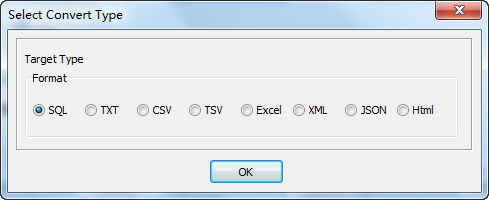
Select SQL file type.
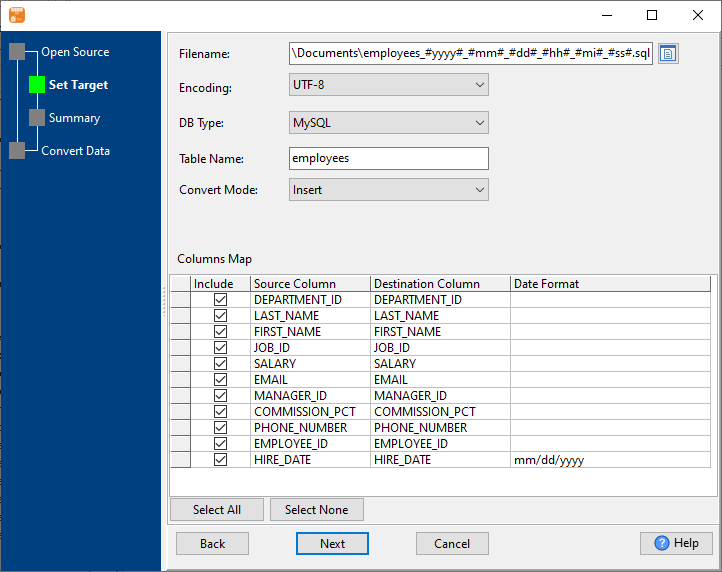
1. Enter Redshift SQL query.

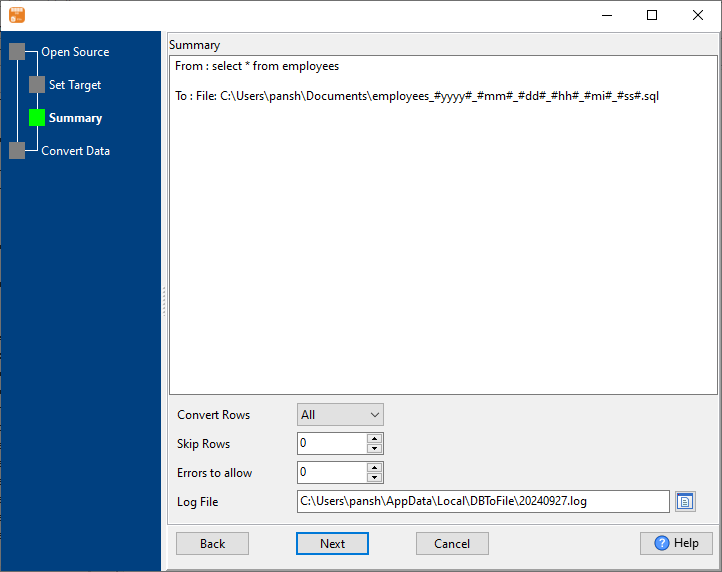
2. Set SQL file options. Enter filename template, including date, #yyyy# is for current year, #mm# month, #dd# day, #hh# hour, #mi# minute, #ss# second.
3. Summary.
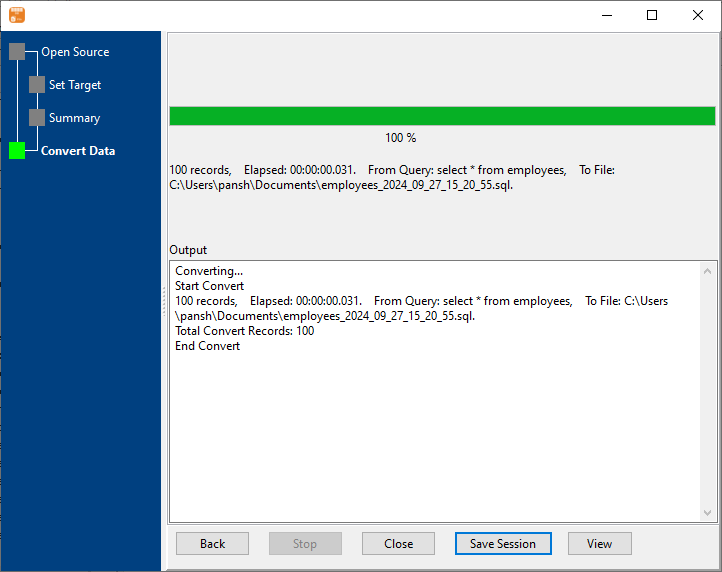
4. Export Redshift query results to SQL file. Dynamically created SQL file name using present system time.
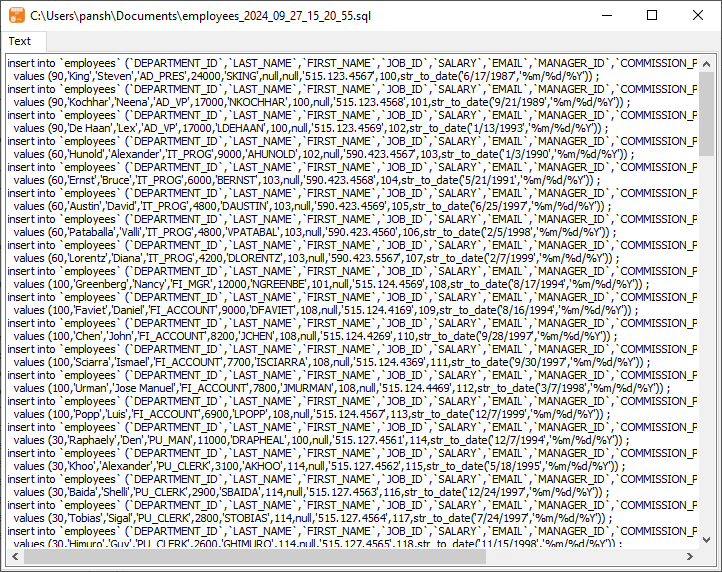
After exporting, you can view output SQL files.
Export Redshift query to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time in command line
Save “Redshift query to SQL” session, then you can:
- Export Redshift query to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time in Windows command line.
- Export Redshift query to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time in Linux command line.
- Export Redshift query to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time in macOS command line.
Set scheduled tasks for exporting Redshift query to SQL using dynamic filename with date and time
Periodic export, keep the old exported SQL files, avoid overwriting them.
You can schedule and automate this “Redshift to SQL” conversion task by:

